How to Set a Static IP Address
August 2021
There are many reasons that you may need to change and set a static IP address for your IP device, such as a managed switch, wireless router, or outdoor access point. One reason is because an installation scenario doesn’t have an active network with DHCP services. Some other reasons you may need to set a static IP are because you use a dedicated web server, host server, VPN, or VoIP services.
Setting static IP addresses can help to avoid network conflicts which could cause certain devices to stop working correctly. However, in most installation scenarios, users will use a regular network and will not need to use a static IP. Setting a static IP address is an advanced networking function, and a basic, fundamental knowledge of TCP/IP is needed.
In general, statically address devices outside of your DHCP pool range, which in most home networks is your router. For reference, the DHCP pool range for TRENDnet products is usually (but not always) 192.168.10.101 to 199.
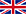
1. Access the Control Panel
In the Windows search bar, type in “ncpa.cpl” and then press enter.

If you are not using Windows 10, follow the steps below instead.
- On your keyboard, press the “Windows” and “R” keys at the same time.
- Enter “ncpa.cpl” in the window that pops up.
Note: Network connections will display the network adapters that are currently connected to your computer.
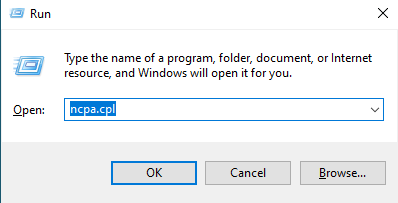
2. Select the Network Adapter
Right click on the network adapter that is currently connected to the device that you are trying to configure. Usually, it will be the adapter with the word “Ethernet” in the name.
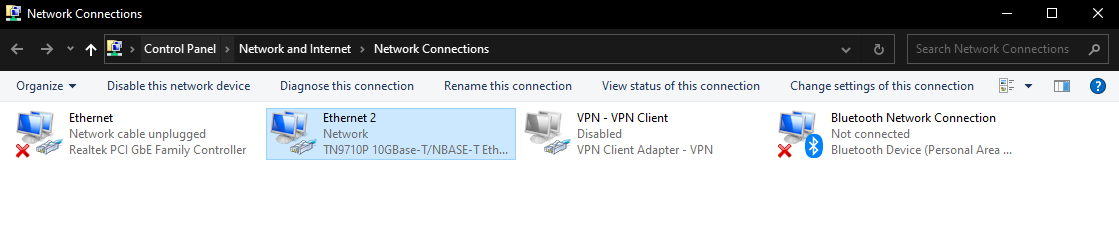
3. Select Properties
Select “Properties” from the drop-down menu.
4. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
Double-click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”.
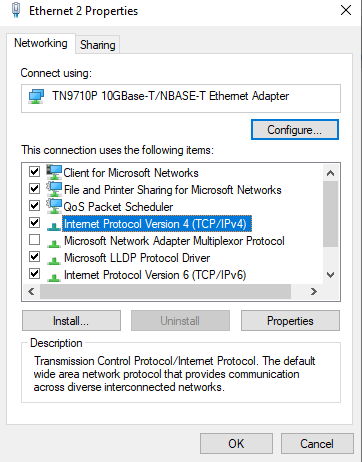
5. Manually enter IP address and subnet mask
Select “Use the following IP Address” and then input the following information in the corresponding fields:
IP address: Check the device that you are connected to in order to locate the IP address. The first three sets of digits should match. For this tutorial, we will use IP address 192.168.10.10.
Subnet mask: The subnet mask between the device that you are trying to connect to needs to be the same as your PC. For this tutorial, we will use subnet mask 255.255.255.0
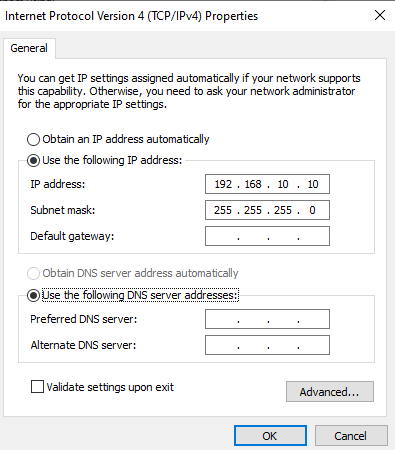
6. Save Settings
Click the OK button on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties” window, and also click the OK button on “Ethernet Properties” window.
Note: The OK buttons must be clicked in both instances or your settings will not be saved.
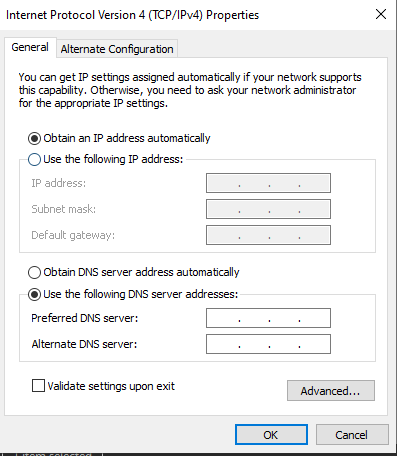
7. Revert Back to DHCP
To set your computer back to DHCP, repeat steps 1-4 again. When you get to the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties” window, click “Obtain an IP address automatically”. This will allow your PC to be assigned a random IP address on your network.
Note: The OK buttons must be clicked in both instances or your settings will not be saved.
Glossary
Operating System
The operating system (often shortened to OS) is the software your computer or mobile device uses to perform basic functions. Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, and Linux are the most popular operating systems for computers and laptops, with Android and iOS for mobile devices.
Browser
A browser (short for web browser) is a software application that allows you to access the internet. Some of the most popular browsers are Chrome, Safari, Edge, Internet Explorer, and Firefox.
Network Adapter
A network adapter allows a device to communicate and connect to a local area network (LAN), the internet, or other computers. Network adapters can be wired or wireless, and they can be visible or hidden from plain sight.
IP Address
An IP address is a unique identifier for devices that access the internet or devices on a local area network. It uses a string of numbers and/or letters with periods or colons. To identify your IP address, type “what is my ip” into a search engine, like Google or Bing. You can also visit whatismyipaddress.com or whatismyip.com.
Dynamic IP address
A dynamic IP address is an IP address that can change over time. Your IP address may change each time you connect. Most IP address assigned by your ISP will be dynamic IP addresses.
Static IP address
A static IP address (also referred to as a manual IP address or static IP configuration) is an IP address that remains unchanged over time. Your IP address remains the same (or static) each time you connect (from the same location). Your IP address may change if you connect to a different network in a different location.
How to Set a Static IP Address |